×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Mazda Parts

My Garage
My Account
Cart
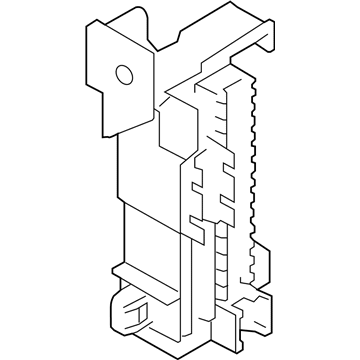
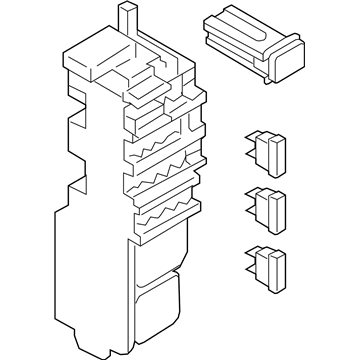
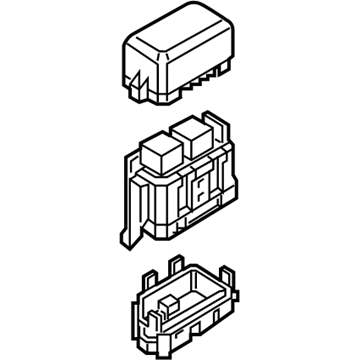
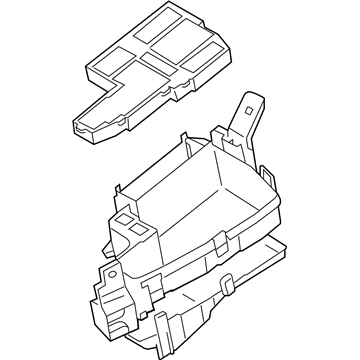
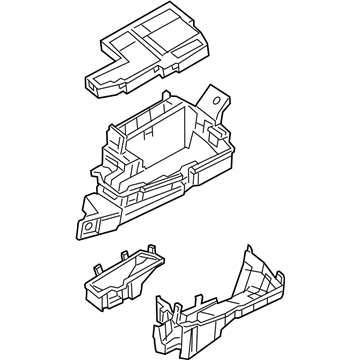
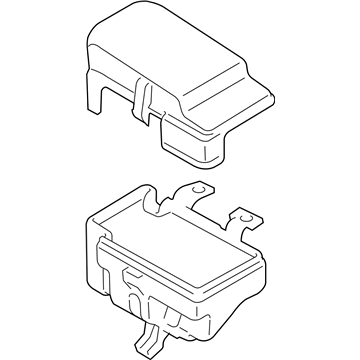
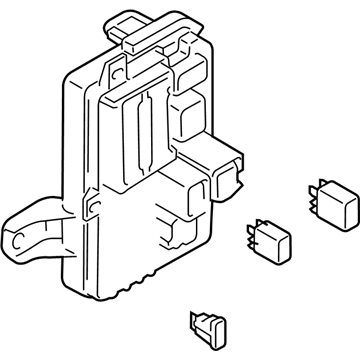
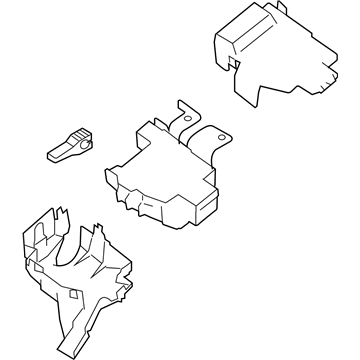
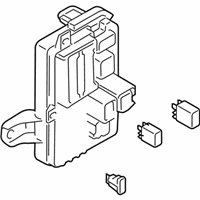
Genuine Mazda 6 Fuse Box
Fuse Holder Box- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
10 Fuse Boxes found
Mazda 6 Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: GHP9-66-730
$16.11 MSRP: $21.50You Save: $5.39 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda 6 Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: GS1D-66-730
$15.40 MSRP: $20.54You Save: $5.14 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda 6 Relay & Fuse Plate Part Number: GBVL-66-750
$27.29 MSRP: $36.40You Save: $9.11 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda 6 Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: GHP9-66-760
$144.68 MSRP: $192.93You Save: $48.25 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda 6 Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: TK48-66-760
$173.84 MSRP: $231.83You Save: $57.99 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda 6 Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: GP9A-66-760A
$216.88 MSRP: $289.22You Save: $72.34 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda 6 Relay & Fuse Plate Part Number: GRT8-66-750
$22.54 MSRP: $30.05You Save: $7.51 (25%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda 6 Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: GP9B-66-730A
$4.32 MSRP: $5.67You Save: $1.35 (24%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda 6 Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: GEG1-66-760
Mazda 6 Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: GS3L-66-760B
Mazda 6 Fuse Box
The Mazda 6 Fuse Box is a safety device that protects all the circuit breakers of the sedan and cuts the power in case a surge poses a threat to parts such as the headlights, door locks, or the sound system. Mounted on the trim of the driver-side dashboard or in the engine bay as part of an inbuilt power module, it stocks blade-style automotive fuses with current ratings of less than 32 volts direct current, with a few slots in more recent versions allowing 42-volt parts to be applied so that additional parts can operate without issue. There are two primary layouts that have emerged over the years; a smaller-size cabin unit designed to fit low-draw features and a larger under-hood assembly that combines high-amp engine relays and normal fuses which minimize the length of wiring and simplify troubleshooting. The two styles use color-coded plug-in blades allowing most Mazda owners to instantly notice a broken link, and some circuits like the ignition-off-draw fuse can be unplugged to prevent battery drain on a long parking stint. Miniature resettable breakers can be found in a few locations, providing an alternative to a replacement component in case there is an overload and a short switch-over to normal operation. Second-generation Mazda 6 drivers who intend to install powerful stereos or LED lights must confirm amperage requirements in the manual and then consider versions to ensure that the selected Fuse Box has sufficient open slots and the appropriate capacity. The only thing that highly often separates a failed Fuse Box from a fully operating electrical system in any Mazda car of the day and age is basic hand tools and labeling the panel.
Looking for Fuse Box with proven quality? Choose OEM Fuse Box. Mazda designs and builds them to strict factory specs. Every piece goes through rigorous quality checks. You'll get parts that fit right and work like new. Shop our huge inventory of OEM Mazda 6 parts. Enjoy the highly competitive prices online. Our site is your one-stop shop. Each genuine 6 part includes a manufacturer's warranty. Buy with confidence. Our return policy is simple and hassle-free. In a rush? Choose expedited delivery at checkout. You'll love the streamlined experience from search to checkout to receiving your order.
Mazda 6 Fuse Box Parts and Q&A
- Q: How is the Fuse Box designed to safeguard electrical circuits, and what should be considered when replacing fuses and fusible links on Mazda 6?A:Fuses, circuit breakers and fusible links are used to protect the electrical circuits of the vehicle, with the main fuse/relay panel in the engine compartment and the interior fuse/relay panel in the passenger compartment. Each fuse has a particular circuit to which it is applied and is marked on the fuse panel and different sizes are used including small, medium, and large fuses all with the same blade terminal design. It is possible to remove medium and large fuses with fingers, whereas it is necessary to use pliers or a plastic fuse-puller tool to remove the small fuses. This is because once an electrical element fails the first step would be to check the fuse, which can be done by a test light to verify a power presence at the terminal ends, and finally, it can be examined visually. Replacement of blown fuses with appropriate type is important because fuses of varying ratings can be interchangeable, but they should not be interchanged with other fuses which have different ratings as each circuit has to be adequately protected. When a replacement fuse fails instantly, the problem behind the fuse, which in most cases is the short circuit caused by faulty wiring, should be taken care of and then subsequent replacement. Fusible links also protect certain circuits, and are found in high-current uses and are developed to melt in case of excess current. On replacement of a blown fusible link the replacement should be of the same specification and in case it blows again then there should be troubleshooting of the circuit before installing the circuit.