×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Mazda Parts

My Garage
My Account
Cart
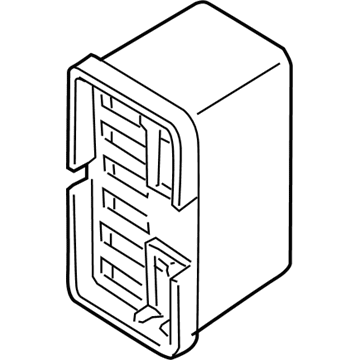
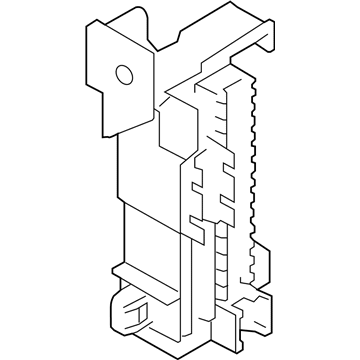
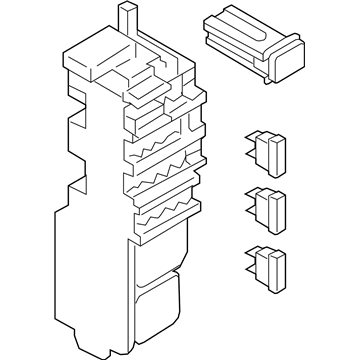
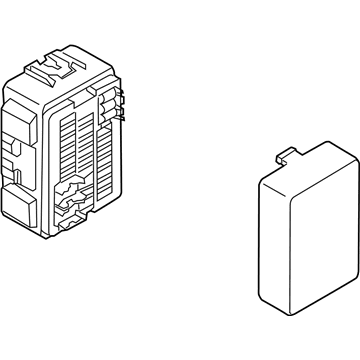
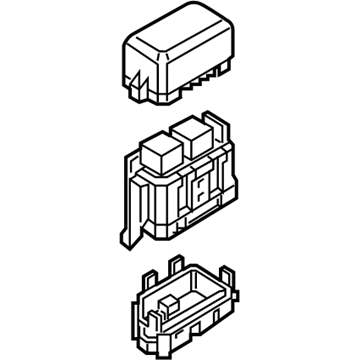
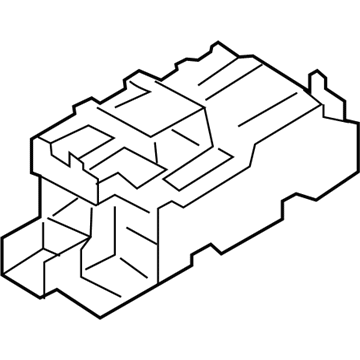
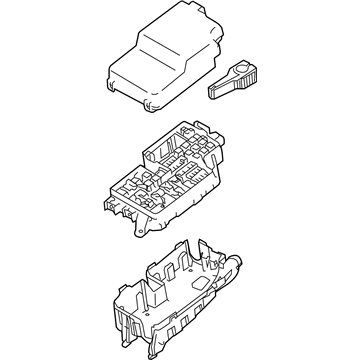
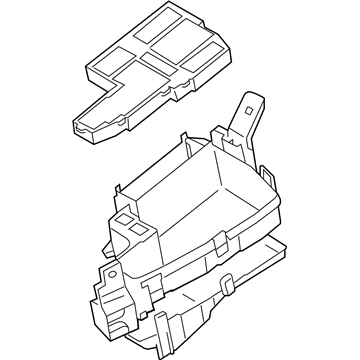
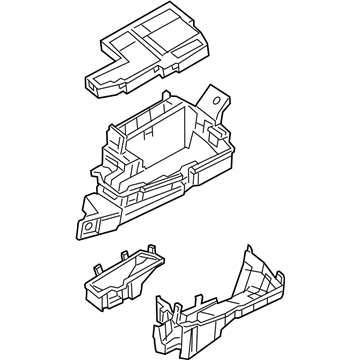
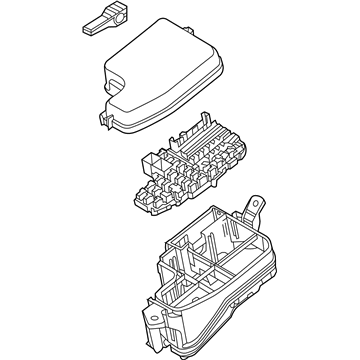
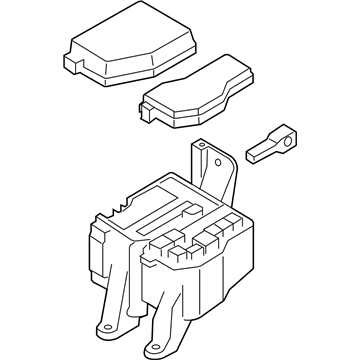
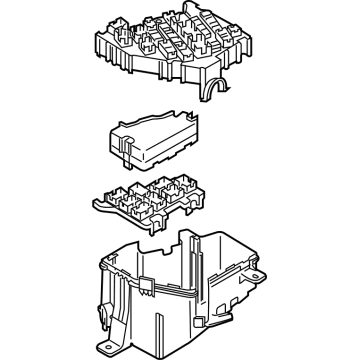
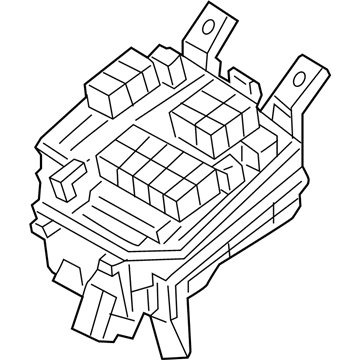
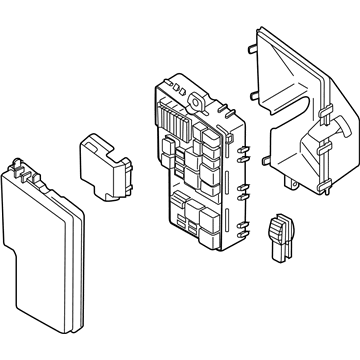
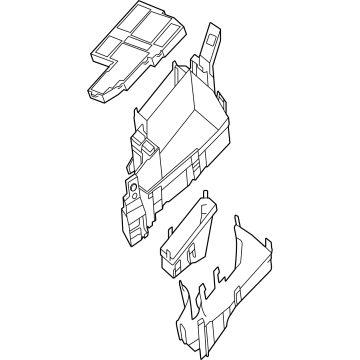
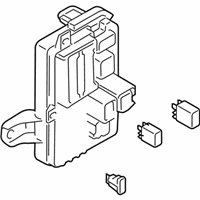
Genuine Mazda Fuse Box
Fuse Holder Box- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
41 Fuse Boxes found
Mazda Fuse Box Part Number: F151-66-730
$7.81 MSRP: $10.41You Save: $2.60 (25%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Fuse
Mazda Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: GHP9-66-730
$16.11 MSRP: $21.50You Save: $5.39 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Fuse
Mazda Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: GS1D-66-730
$15.40 MSRP: $20.54You Save: $5.14 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Fuse
Mazda Fuse Box Part Number: L206-66-730
$21.48 MSRP: $28.64You Save: $7.16 (25%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Fuse
Mazda Relay & Fuse Plate Part Number: GBVL-66-750
$27.29 MSRP: $36.40You Save: $9.11 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Relay; Relay Fuse Plate
Mazda Fuse Box Part Number: BCKA-66-730
$28.64 MSRP: $38.19You Save: $9.55 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Fuse; Fuse Box, Fuse Holder
Mazda Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: BBM6-66-760
$122.08 MSRP: $162.80You Save: $40.72 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Main Fuse
Mazda Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: GHP9-66-760
$144.68 MSRP: $192.93You Save: $48.25 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Main Fuse
Mazda Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: TK48-66-760
$173.84 MSRP: $231.83You Save: $57.99 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Main Fuse
Mazda Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: B62S-66-760
$197.70 MSRP: $263.65You Save: $65.95 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Main Fuse; Fuse & Relay Box
- Replaces: BHR1-66-760, BHR1-66-760A
Mazda Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: TK21-66-760
$184.80 MSRP: $246.46You Save: $61.66 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Main Fuse
Mazda Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: TK24-66-760
$184.80 MSRP: $246.46You Save: $61.66 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Main Fuse
Mazda Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: TG21-66-760
$189.89 MSRP: $253.24You Save: $63.35 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Main Fuse
Mazda Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: NE51-66-760B
$212.59 MSRP: $283.51You Save: $70.92 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Main Fuse
- Replaces: NE51-66-760A
Mazda Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: BCKA-66-760
$212.98 MSRP: $284.02You Save: $71.04 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Main Fuse; Fuse & Relay Box
Mazda Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: EH44-66-760B
$201.44 MSRP: $268.63You Save: $67.19 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Main Fuse
Mazda Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: KD45-66-760A
$218.45 MSRP: $291.32You Save: $72.87 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Main Fuse
Mazda Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: TE71-66-760A
$207.56 MSRP: $276.81You Save: $69.25 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Block, Main Fuse
Mazda Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: BFD2-66-760
Product Specifications- Other Name: Block, Main Fuse
Mazda Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: BBM5-66-760B
Product Specifications- Other Name: Block, Main Fuse
- Replaces: BBM5-66-760A
| Page 1 of 3 |Next >
1-20 of 41 Results
Mazda Fuse Box
The Mazda Fuse Box provides protection to every circuit in the vehicle, immediately shutting off power when there is a surge of current beyond what is safe for the vehicle's lights, infotainment and control units. Mazda cars have received worldwide acclaim for their fun-to-drive characteristics, Skyactiv engines that sip fuel but pack a punch, and the signature Kodo styling that appears to be in motion even when at a halt. Inside, Mazda provides i-Activsense features such as lane keeping and radar cruise to help drivers keep their eyes on the road and stay alert, while available all-wheel drive demonstrates its prowess on bumpy roads and in the rain. Owners also like the way in which Mazda combines eco-friendly mild hybrid and electric technologies with the same fun-to-drive spirit first introduced in its rotary heritage. Hidden under that sleek bodywork, the Fuse Box incorporates labeled blade fuses and a resettable circuit breaker to create a small power hub that fits every model of Mazda, from compact cars to capable SUVs. One section is housed in the engine bay for handling heavy loads while another is kept close to the steering wheel for quick checks allowing drivers to find and replace a blown fuse in minutes. An ignition-off draw slot even helps in saving battery charge when parking for a long time. Thanks to solid construction and accessibility, the Mazda Fuse Box keeps future upgrades such as upgraded stereos or LED lighting running safely without fuss.
You'll get great performance and real durability when you pick genuine OEM Fuse Box. Mazda builds these using high-quality materials and official factory methods to ensure they hold up mile after mile. You deserve that Mazda reliability without the headache of cheap knockoffs. It is easy to find exactly what you need in our huge inventory of genuine parts. Plus, every OEM part carries a real manufacturer's warranty for your peace of mind. You will love our low prices too. Order today and we will ship your brand-new parts fast. They often reach your door in just a few days.
Mazda Fuse Box Parts and Q&A
- Q: How is the Fuse Box used to safeguard a vehicle's electrical circuits and what should be done in the event of a fuse failure on Mazda 3?A:A combination of fuses, circuit breakers, and fusible links protect the electrical circuits of the vehicle, the main fuse/relay panel of which is located in the engine compartment and the interior fuse/relay panel of which is located in the passenger compartment (2009 and earlier models have it below the passenger side of the instrument panel and 2010 and later models have it underneath the driver side). There are small, medium, and large fuses used in the fuse blocks with the same blade terminal design; the medium and large fuses may be removed by hand, but the small fuses must be removed with a plier or fuse-puller tool made of plastic. Whenever there is any electrical component failure, it is the first step to check the fuse and the most effective way of doing so is to check the presence of power on the exposed terminal tips of each fuse using a test light, where one side has power and the other side has no power then the fuse is blown and this can also be detected visually. It is also important to ensure that the blown fuses are replaced with the correct type because the different rating fuses might fit physically but still different as this will be the correct one to protect the respective electrical circuits, and the value in the amperage should be carved into the top of the fuse body. When a replacement fuse fails instantly, it must not be replaced until the fault is located and corrected as it is normally a short circuit due to a damaged wire. Also, there are circuits that have fusible links that provide protection against overcurrent, and which are found in a circuit that is not normally fused, or where the current can be very high, as in the connection between the alternator and the battery; the fusible link is designed to melt away should excessive current be applied to it, and then troubleshooting becomes necessary before installing another circuit.
- Q: How is the Fuse Box designed to safeguard electrical circuits, and what should be considered when replacing fuses and fusible links on Mazda 6?A:Fuses, circuit breakers and fusible links are used to protect the electrical circuits of the vehicle, with the main fuse/relay panel in the engine compartment and the interior fuse/relay panel in the passenger compartment. Each fuse has a particular circuit to which it is applied and is marked on the fuse panel and different sizes are used including small, medium, and large fuses all with the same blade terminal design. It is possible to remove medium and large fuses with fingers, whereas it is necessary to use pliers or a plastic fuse-puller tool to remove the small fuses. This is because once an electrical element fails the first step would be to check the fuse, which can be done by a test light to verify a power presence at the terminal ends, and finally, it can be examined visually. Replacement of blown fuses with appropriate type is important because fuses of varying ratings can be interchangeable, but they should not be interchanged with other fuses which have different ratings as each circuit has to be adequately protected. When a replacement fuse fails instantly, the problem behind the fuse, which in most cases is the short circuit caused by faulty wiring, should be taken care of and then subsequent replacement. Fusible links also protect certain circuits, and are found in high-current uses and are developed to melt in case of excess current. On replacement of a blown fusible link the replacement should be of the same specification and in case it blows again then there should be troubleshooting of the circuit before installing the circuit.