×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Mazda Parts

My Garage
My Account
Cart
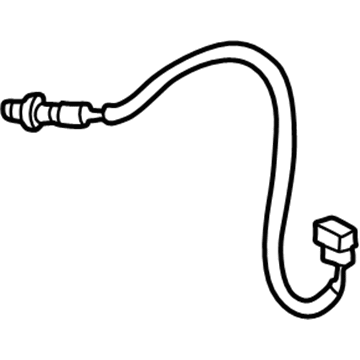
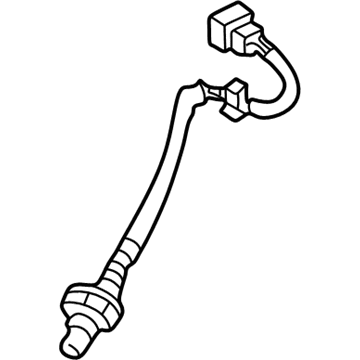
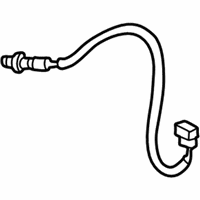
Genuine Mazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor
Oxygen O2 Sensor- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
15 Oxygen Sensors found
Mazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor Part Number: KJ02-18-861C-9U
$168.33 MSRP: $224.48You Save: $56.15 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor Part Number: KJ04-18-861B-9U
$185.00 MSRP: $246.72You Save: $61.72 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor Part Number: KL1C-18-861-9U
$187.56 MSRP: $250.13You Save: $62.57 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor Part Number: KL1D-18-861-9U
$187.56 MSRP: $250.13You Save: $62.57 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor Part Number: TA36-18-861B-9U
$193.31 MSRP: $257.80You Save: $64.49 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor Part Number: KJ01-18-861A-9U
$191.45 MSRP: $255.31You Save: $63.86 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor Part Number: KJ03-18-861B-9U
$207.55 MSRP: $276.80You Save: $69.25 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor Part Number: KL62-18-861A-9U
$247.06 MSRP: $329.48You Save: $82.42 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor Part Number: KLL5-18-861B-9U
$39.85 MSRP: $52.31You Save: $12.46 (24%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor Part Number: TA37-18-861E-9U
$39.33 MSRP: $51.63You Save: $12.30 (24%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor Part Number: FS2V-18-861B-9U
Mazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor Part Number: KL1E-18-861A-9U
Mazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor Part Number: KL61-18-861A-9U
Mazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor Part Number: KLL6-18-861C
Mazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor Part Number: TA34-18-861B-9U
Mazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor
Looking for Oxygen Sensor with proven quality? Choose OEM Oxygen Sensor. Mazda designs and builds them to strict factory specs. Every piece goes through rigorous quality checks. You'll get parts that fit right and work like new. Shop our huge inventory of OEM Mazda Millenia parts. Enjoy the highly competitive prices online. Our site is your one-stop shop. Each genuine Millenia part includes a manufacturer's warranty. Buy with confidence. Our return policy is simple and hassle-free. In a rush? Choose expedited delivery at checkout. You'll love the streamlined experience from search to checkout to receiving your order.
Mazda Millenia Oxygen Sensor Parts and Q&A
- Q: How does the oxygen sensor interact with exhaust gases and what are the implications of its voltage signals on air/fuel ratio on Mazda Millenia?A:The oxygen sensor reacts with exhaust gases producing a voltage signal which is deciphered by the ECU to estimate the air fuel ratio whereby a low voltage value would indicate a lean condition whereas a high value would indicate a rich condition. The sensor is normally mounted on the exhaust manifold or pipes but in the case of turbocharged engines, the sensor is mounted inside the turbocharger. Certain Mazda engines can also possess various sensors such as front and rear sensors or pre-catalytic converter sensor and post-catalytic converter sensor to measure efficiency. In order to check the sensor output voltage, the engine must be running, and measurements of the sensor terminals should be taken, with certain voltage range of rich or lean conditions. In case of readings outside the ranges of specifications, the sensor is to be replaced. In the case of heater element resistance testing, then the sensor has to be disconnected, and the resistance between special terminals should be measured, with certain values of resistance at a given temperature being expected. When the readings are off range then the sensor might require replacement. To remove, the splash shielding that may be required should be removed, then the sensor wire connection should be detached, and the sensor should be loosened at the place where it is located. Other procedures in a turbocharged engine are switching off the battery and the sensor in the turbocharger. Removal should be reversed in regards to installation whereby proper specifications of torque are observed.