×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Mazda Parts

My Garage
My Account
Cart
Genuine Mazda MX-5 Miata Oxygen Sensor
Oxygen O2 Sensor- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
7 Oxygen Sensors found
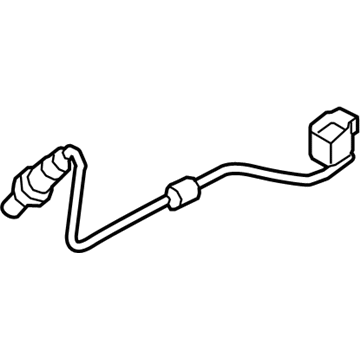
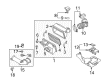
Mazda MX-5 Miata Oxygen Sensor Part Number: P51C-18-861
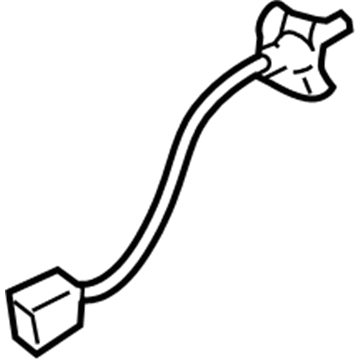
$209.20 MSRP: $278.99You Save: $69.79 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda MX-5 Miata Oxygen Sensor Part Number: P517-18-8GX
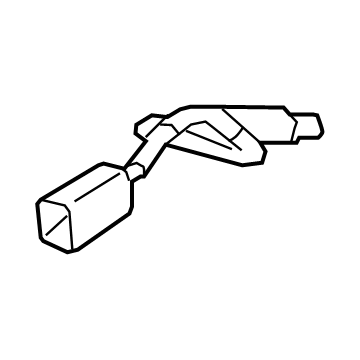
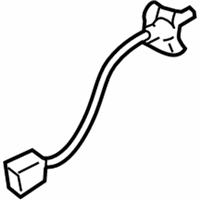
$225.86 MSRP: $301.21You Save: $75.35 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda MX-5 Miata Oxygen Sensor Part Number: LFG2-18-861B-9U
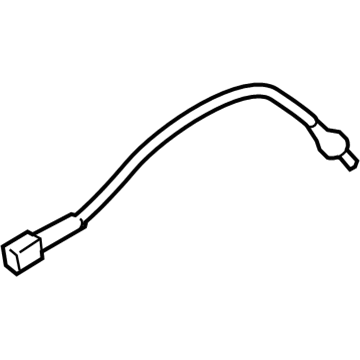
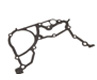
$244.03 MSRP: $325.43You Save: $81.40 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda MX-5 Miata Oxygen Sensor Part Number: P51B-18-8GX
$267.59 MSRP: $356.85You Save: $89.26 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda MX-5 Miata Oxygen Sensor Part Number: LFG1-18-8G1A
$286.51 MSRP: $382.09You Save: $95.58 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda MX-5 Miata Oxygen Sensor Part Number: P518-18-861
$312.26 MSRP: $416.43You Save: $104.17 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysMazda MX-5 Miata Oxygen Sensor Part Number: LFN1-18-8G1A
$495.98 MSRP: $666.76You Save: $170.78 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Mazda MX-5 Miata Oxygen Sensor
Looking for Oxygen Sensor with proven quality? Choose OEM Oxygen Sensor. Mazda designs and builds them to strict factory specs. Every piece goes through rigorous quality checks. You'll get parts that fit right and work like new. Shop our huge inventory of OEM Mazda MX-5 Miata parts. Enjoy the highly competitive prices online. Our site is your one-stop shop. Each genuine MX-5 Miata part includes a manufacturer's warranty. Buy with confidence. Our return policy is simple and hassle-free. In a rush? Choose expedited delivery at checkout. You'll love the streamlined experience from search to checkout to receiving your order.
Mazda MX-5 Miata Oxygen Sensor Parts and Q&A
- Q: What is the function and operation of the oxygen sensor in monitoring exhaust gases on Mazda MX-5 Miata?A:The oxygen sensor measures exhaust gases prior to their being flowing through the Catalytic Converter, and subsequent models had a subsequent sensor to aid in efficiency comparison by the PCM. The sensor produces a voltage signal that ranges between 0.1 volts (lean mixture) and 0.9 volts (rich mixture) to enable the PCM adjust the air/fuel mixture ratio preferably keeping the ratio at 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel to achieve optimum emissions control. The sensor is not voltaged until it reaches about 600 degrees F at which point the PCM is used in open loop. In case the voltage of the main sensor does not reach 0.70 volts in higher RPMs when the engine is warmed up, a Code 15 is programmed. To ensure proper operation of a sensor, clean electrical connections, free air supply, proper operating temperature and use of unleaded fuel are also vital. When servicing, care should be taken not to damage the attached pigtail and electrical connector, to keep contaminants off and the silicone boot properly in place. To replace it, one may recommend first warming the engine to facilitate the extraction of the sensor, then disconnecting the negative battery terminal, then raising the vehicle and then disconnecting the electrical connector, remove the sensor, apply anti-seize paste to the threads, install and tighten the new sensor, then reconnect the electrical connector, then lower the vehicle then reconnect the negative battery terminal.
Related Mazda MX-5 Miata Parts
Browse by Year
2023 Oxygen Sensor 2022 Oxygen Sensor 2021 Oxygen Sensor 2020 Oxygen Sensor 2019 Oxygen Sensor 2018 Oxygen Sensor 2017 Oxygen Sensor 2016 Oxygen Sensor 2015 Oxygen Sensor 2014 Oxygen Sensor 2013 Oxygen Sensor 2012 Oxygen Sensor 2011 Oxygen Sensor 2010 Oxygen Sensor 2009 Oxygen Sensor 2008 Oxygen Sensor 2007 Oxygen Sensor 2006 Oxygen Sensor