×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Mazda Parts

My Garage
My Account
Cart
Genuine Mazda Protege Relay Boxes
Relay Block- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
1 Relay Boxes found
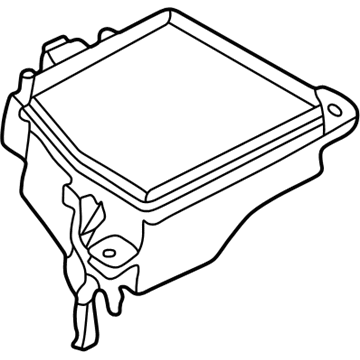
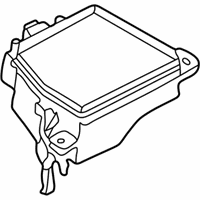
Mazda Protege Fuse Box Main Part Number: B25D-66-760D
Mazda Protege Relay Boxes
Looking for Relay Boxes with proven quality? Choose OEM Relay Boxes. Mazda designs and builds them to strict factory specs. Every piece goes through rigorous quality checks. You'll get parts that fit right and work like new. Shop our huge inventory of OEM Mazda Protege parts. Enjoy the highly competitive prices online. Our site is your one-stop shop. Each genuine Protege part includes a manufacturer's warranty. Buy with confidence. Our return policy is simple and hassle-free. In a rush? Choose expedited delivery at checkout. You'll love the streamlined experience from search to checkout to receiving your order.
Mazda Protege Relay Boxes Parts and Q&A
- Q: What role do Relay Boxes play in the operation of electrical accessories, and how can they be tested for defects on Mazda Protege?A:The vehicle has a number of electrical accessories which use relays to pass electrical signals to the components with the low-current control circuit to control a high-current power circuit, (fuel injection system), horns, starter, and fog lamps, etc.) An incorrectly operating relay will not allow the corresponding component to operate, the majority of the relays are found in the engine compartment and interior fuse/relay boxes, one electrical center is below the left end of the instrument panel. In case of a faulty relay, it can be removed and testable either by a particular procedure or by a dealer or repair shop, and faulty relays need to be replaced as a unit. The relay in most of these vehicles are ISO relays with numbered terminals denoting the connections and functions of the circuit with two simple terminal layouts. The control circuit is attached to the relay coil, with the other terminals attached to the power circuit, whereby supply of current to the circuit loads through bigger contacts is achieved by energizing the relay and producing a magnetic field. The control circuit is usually in terminals 85 and 86 and special connections may be necessary when using a diode or resistor. Terminal 30 is attached to the source of battery voltage, and terminal 87 is attached to the ground side of the circuit. As a test of continuity, the ohmmeter can be used to test continuity using the control coil and verify that the resistance has the correct values and that its behavior is as desired with or without the resistor or diode. Also, there should be no continuity between the terminal 30 and 87 when the relay is not energized and when the relay is energized by using the jumper wires continuity between the power circuit terminals should be also checked. In case of failure in any of the tests, then the relay must be changed.