×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Mazda Parts

My Garage
My Account
Cart
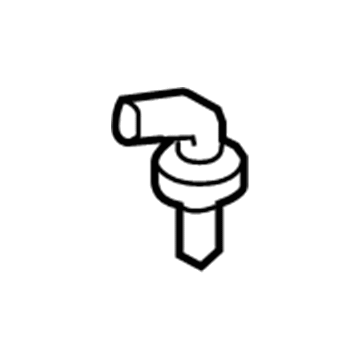
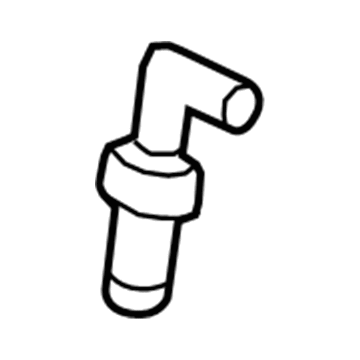
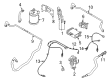
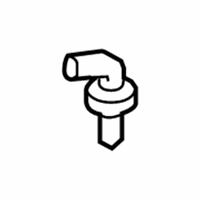
Genuine Mazda PCV Valve
Position Crank Ventilation Valve- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
35 PCV Valves found
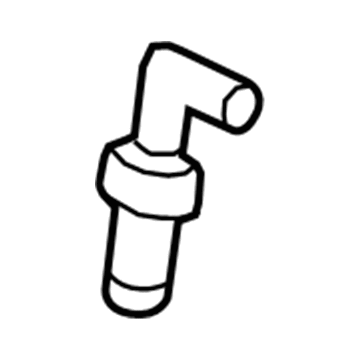
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: 1F22-13-890A
$24.39 MSRP: $32.52You Save: $8.13 (25%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: PCV Valve, Heated
- Replaces: 1F22-13-890, AJ03-13-89X
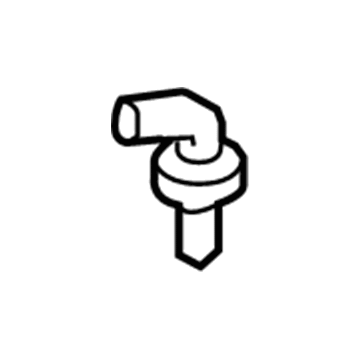
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: AJC1-13-890B
$13.90 MSRP: $18.53You Save: $4.63 (25%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Valve, P.C.V.; PCV Valve
- Replaces: 1F72-13-890, AJC1-13-890A, AJC1-13-890
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: PY01-13-890
$15.53 MSRP: $20.70You Save: $5.17 (25%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Valve, P.C.V.
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: L356-13-890
$18.89 MSRP: $25.19You Save: $6.30 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Valve, P.C.V.
- Replaces: 1F70-13-890, ZZC0-13-890
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: L3K9-13-890
$23.30 MSRP: $31.07You Save: $7.77 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Valve, P.C.V.
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: PE01-13-890
$14.64 MSRP: $19.51You Save: $4.87 (25%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Valve, P.C.V.
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: L325-13-890A
$17.20 MSRP: $22.93You Save: $5.73 (25%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Valve, P.C.V.
- Replaces: LF13-13-890
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: LF15-13-890
$12.23 MSRP: $16.30You Save: $4.07 (25%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Valve, P.C.V.
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: B603-13-890
$24.56 MSRP: $32.76You Save: $8.20 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Valve, PCV
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: BP05-13-890
$26.18 MSRP: $34.91You Save: $8.73 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Valve, PCV
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: E301-13-890A
$26.25 MSRP: $35.01You Save: $8.76 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Valve, PCV
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: G601-13-890
$25.29 MSRP: $33.72You Save: $8.43 (25%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Valve, PCV
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: NF01-13-890
$29.15 MSRP: $38.87You Save: $9.72 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Valve, PCV
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: N3A1-13-890
$31.55 MSRP: $42.08You Save: $10.53 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Valve, PCV
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: JE96-13-890
$29.38 MSRP: $39.18You Save: $9.80 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Valve, PCV
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: YF71-13-890A
$7.96 MSRP: $78.15You Save: $70.19 (90%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Valve, P.C.V.
- Replaces: YF71-13-890
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: CY01-13-890
$90.53 MSRP: $120.72You Save: $30.19 (26%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Valve, P.C.V.
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: AJ95-13-890A
$10.64 MSRP: $14.18You Save: $3.54 (25%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Valve, PCV
- Replaces: AJ95-13-890
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: KL01-13-890
Product Specifications- Other Name: Valve, PCV
Mazda PCV Valve Part Number: GYY1-13-890
Product Specifications- Other Name: Valve, PCV
| Page 1 of 2 |Next >
1-20 of 35 Results
Mazda PCV Valve
The Mazda PCV Valve helps to maintain a clean pressure balance within each Mazda engine by recycling crankcase gases for smooth power delivery and reduced emissions. Positioned between the rocker cover and intake, the PCV Valve consists of a one-way gate that remains in a nearly closed position at idle condition to protect the air-fuel mixture and opens as the throttle increases to draw the blow-by vapors back for a second burn to prevent sludge, sealing the piston rings and blocking flames from backfires. This is a very clever routing, as it reduces oil consumption, keeps the internal parts cleaner, and supports the eager throttle response drivers are applied to, and a quick shake test assures the PCV Valve is free and functional. Complementing this device, Mazda stands out through Skyactiv technology which extracts strong performance from each drop of fuel, Kodo Soul of Motion styling that gives every curve a sense of life, and i-Activsense safety aids that use radar and cameras to keep watch and lend confidence. Rigorous i-Activ AWD trials on rough surfaces are evidence of Mazda durability, and new electric and mild hybrid options are evidence of its commitment to next-generation efficiency. Lightweight chassis tuning and precise steering mean Mazda vehicles feel agile on winding roads but relaxed in city traffic, and thoughtful cabins combine intuitive tech and enduring comfort. From nimble compacts to versatile sport utility vehicles, Mazda continues to provide practical, stylish, and fun transportation that rewards every drive.
You'll get great performance and real durability when you pick genuine OEM PCV Valve. Mazda builds these using high-quality materials and official factory methods to ensure they hold up mile after mile. You deserve that Mazda reliability without the headache of cheap knockoffs. It is easy to find exactly what you need in our huge inventory of genuine parts. Plus, every OEM part carries a real manufacturer's warranty for your peace of mind. You will love our low prices too. Order today and we will ship your brand-new parts fast. They often reach your door in just a few days.
Mazda PCV Valve Parts and Q&A
- Q: Where is the PCV valve located and how do you remove and install it on Mazda 3?A:In order to get the timing cover and timing belt off, begin by removing the sprocket on the camshaft. The second step is to loosen the bolts and loosen the gasket seal with a screwdriver before detaching the cover and the cylinder head. Installation To be installed, the mating surfaces of the gasket material should be cleaned. Install the retaining bolts with a new gasket and screw the housing cover with the gasket making sure to tighten the screw to the recommended torque. Installation Complete the steps of removal in reverse.
- Q: What is the function and importance of the PCV valve on Mazda B2200?A:A PCV valve works to pump the blow-by gases out of the crankcase to the intake manifold which is combusted in the cylinders; it is a PCV valve, an oil separator, and connecting hoses. Air comes in through the air cleaner to the rocker cover is ventilated, and flows to the oil separator, and then to the PCV valve, which functions as per air pressure variations between the intake manifold and the rocker cover. The PCV valve is also important because it controls the amount of gas that is re-introduced into the combustion chamber; it also partially closes at low engine revolutions to restrict the amount of gas flow and opens further as the engine speed rises. A valve blockage will not allow the gases to escape the crankcase resulting in pressure build-up that can cause the gases to escape through weak seals or gaskets resulting in oil spillage and formation of sludge. To test the component, disconnect the hose of the PCV valve, turn the engine to 700-1000 rpm and put a finger on the end of the valve to test the presence of a vacuum; in the absence of this, the valve must be changed. To remove, install, discharge the hose, unscrew the valve out of its fitting, screw in the new one, and reconnect the hose.
Related Mazda Parts
Browse by Model
2 PCV Valve 3 PCV Valve 323 PCV Valve 5 PCV Valve 6 PCV Valve 626 PCV Valve 929 PCV Valve B2000 PCV Valve B2200 PCV Valve B2300 PCV Valve B2500 PCV Valve B2600 PCV Valve B3000 PCV Valve B4000 PCV Valve CX-3 PCV Valve CX-30 PCV Valve CX-5 PCV Valve CX-50 PCV Valve CX-7 PCV Valve CX-9 PCV Valve GLC PCV Valve MPV PCV Valve MX-3 PCV Valve MX-5 Miata PCV Valve MX-6 PCV Valve Miata PCV Valve Millenia PCV Valve Navajo PCV Valve Protege PCV Valve Protege5 PCV Valve RX-7 PCV Valve Tribute PCV Valve